Related guidance:
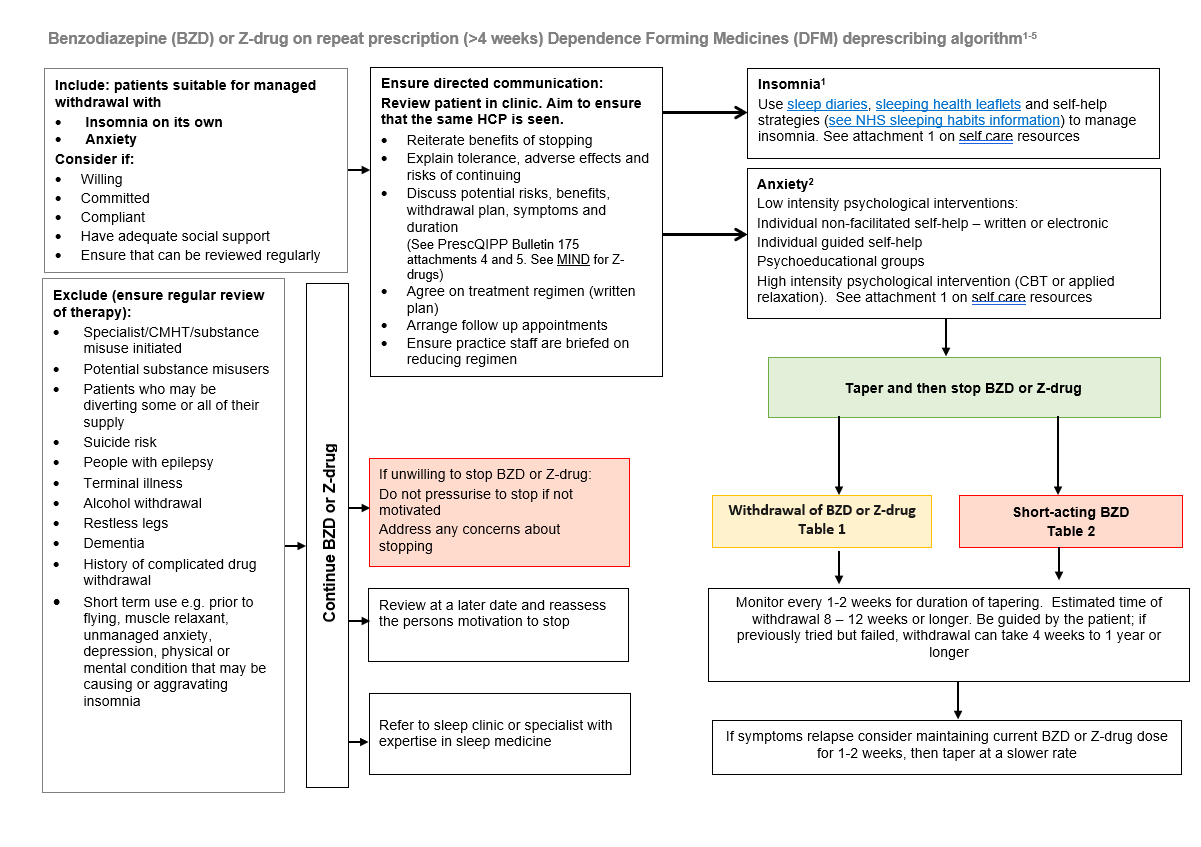
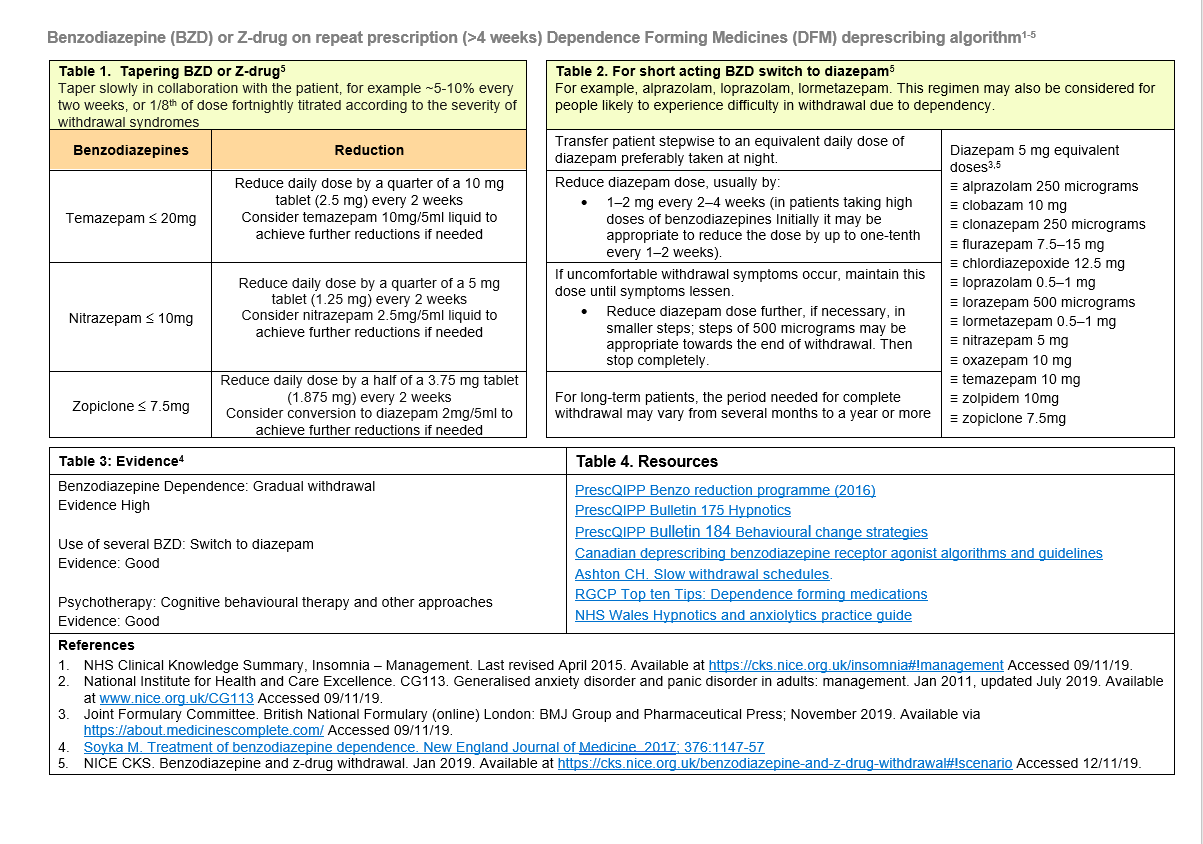
Benzodiazepine (BZD) or Z-drug on repeat prescription (>4 weeks) Dependence Forming Medicines (DFM) deprescribing algorithm
- Good sleep hygiene should be established in all people with insomnia. This aims to make people more aware of behavioural, environmental, and temporal factors that may be detrimental or beneficial to sleep.
- Hypnotic medication should be avoided if possible due to potential for significant adverse effects.
- Cognitive behavioural therapy for insomnia (CBT-I) is recommended for treatment of both short- and long-term insomnia in adults of all ages — unlike medication, benefits associated with CBT-I persist on completion of treatment.
- GP practices have access to cognitive behavioural therapy for insomnia (CBT-I) via referral to Somerset Foundation Trust (SFT) Talking Therapies.
- If, following an assessment by Talking Therapies, CBT-I is recommended then patients are given access to Silver Cloud’s online Space from Insomnia and Sleep Issues programme.
- Patient decision aid full version: Should I Stop my benzodiazepine or z-drug?
- Patient decision aid summary: Should I Stop my benzodiazepine or z-drug?
Anxiety disorders Quality standard (QS53 February 2014)
Daridorexant for treating long-term insomnia Technology appraisal guidance (TA922 October 2023)
- It is now an offence to drive with any of 17 controlled drugs above a specified level in your blood – this includes illegal and medical drugs.
Prescription medicines include
- amphetamine, for example dexamphetamine or selegiline
- clonazepam
- diazepam
- flunitrazepam
- lorazepam
- methadone
- morphine or opiate and opioid-based drugs, for example codeine, tramadol or fentanyl
- oxazepam
- temazepam
All Prescriptions for hypnotics should be limited to 7-14 days supply and not transferred to repeat.
Tolerance can develop within 3 to 14 days of continuous use.
Benzodiazepines (STOPP Criteria)
- for ≥ 4 weeks (no indication for longer treatment; risk of prolonged sedation, confusion, impaired balance, falls, road traffic accidents; all benzodiazepines should be withdrawn gradually if taken for more than 4 weeks as there is a risk of causing a benzodiazepine withdrawal syndrome if stopped abruptly).
NHS Somerset hypnotics and anxiolytics
| Therapeutic Area | Formulary Choices | Cost for 28 (unless otherwise stated) | Rationale for decision / comments |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hypnotics, sedatives and anxiolytics, non-benzodiazepine | Hypnotics, sedatives and anxiolytics cause physical and psychological dependence and tolerance. Should be reserved for short courses to alleviate acute conditions after causal factors have been established. | ||
| Taking zolpidem is associated with a risk of impaired driving ability the next day. See MHRA (December 2014) for Zolpidem: risk of drowsiness and reduced driving ability. | |||
| Zolpidem | 5mg tablet: £1.61 | 5mg (elderly) - 10mg (adult) to be taken at bedtime. | |
| 10mg tablet: £1.26 | |||
| Zopiclone | 3.75mg tablet: £1.45 | 3.75mg (elderly) - 7.5mg (adult) to be taken at bedtime. | |
| 7.5mg tablet: £1.33 | |||
| Melatonin | 2mg prolonged release tablet: £6.53 (30) | Indicated as monotherapy for the short-term treatment (up to 13 weeks) of primary insomnia characterised by poor quality of sleep in patients who are aged 55 or over. It is also approved for use in patients with Parkinson's disease related insomnia (off-label). NHS Somerset classify as Amber for hemicrania continua. Melatonin for insomnia for children, adolescents and adults aged below 55 will remain a BLACK drug (not recommended) and any treatment initiated by an acute trust specialist should remain the prescribing and monitoring responsibility of that specialist as per Traffic light guidance. |
|
| NHS Somerset classify Clomethiazole for alcohol withdrawal as Red (specialist prescribing only) and for all other indications as Black (not recommended) as per Traffic light guidance. | |||
| The paediatric indication for chloral hydrate (for children aged 2 years and older) and cloral (previously chloral) betaine (children aged 12 years and older) has been restricted to short-term treatment (maximum 2 weeks) of severe insomnia only when the child or adolescent has a suspected or definite neurodevelopmental disorder and when the insomnia is interfering with normal daily life. Chloral hydrate and cloral betaine should only be used when other therapies (behavioural and pharmacological) have failed. See MHRA (October 2021) for Chloral hydrate, cloral betaine (Welldorm): restriction of paediatric indication. | |||
| NHS Somerset classify Chloral hydrate and Chloral betaine as Black (not recommended) as per Traffic light guidance. | |||
| Hypnotics, sedatives and anxiolytics, benzodiazepine | Benzodiazepines and opioids can both cause respiratory depression, which can be fatal if not recognised in time. Only prescribe together if there is no alternative and closely monitor patients for signs of respiratory depression. See MHRA (March 2020) for Benzodiazepines and opioids: reminder of risk of potentially fatal respiratory depression. | ||
| Benzodiazepines are indicated for the short term relief of anxiety that is severe, disabling, or causing the patient unacceptable distress, occurring alone or in association with insomnia or short term psychosomatic, organic or psychotic illness. The use of benzodiazepines to treat short term mild anxiety is inappropriate. Benzodiazepines should only be used to treat insomnia when it is severe, disabling or causing the patient extreme distress. |
|||
| Temazepam | 10mg tablet: £23.61 | 10mg (elderly) - 20mg (adult) to be taken at bedtime. | |
| 20mg tablet: £24.25 | |||
| Diazepam | 2mg tablet: £0.79 | 5-15mg (adult) to be taken at bedtime. | |
| 5mg tablet: £0.81 | |||
| Orexin receptor antagonist | Daridorexant as Quviviq® | 25mg tablet: £42.00 (30) | For treating insomnia in adults with symptoms lasting for 3 nights or more per week for at least 3 months, and whose daytime functioning is considerably affected, only if: • cognitive behavioural therapy for insomnia (CBTi) has been tried but not worked, or • CBTi is not available or is unsuitable. The length of treatment should be as short as possible. Treatment should be assessed within 3 months of starting and should be stopped in people whose long-term insomnia has not responded adequately. If treatment is continued, assess whether it is still working at regular intervals. Adult: 50 mg once per night, taken orally in the evening within 30 minutes before going to bed. People with moderate hepatic impairment or when used with moderate CYP3A4 inhibitors, the recommended dose is one tablet of 25 mg once per night. The consumption of grapefruit or grapefruit juice in the evening should be avoided. If a patient forgets to take dose at bedtime, that dose should not be taken during the night. The maximum daily dose is 50 mg. Treatment can be stopped without down-titration. |
| 50mg tablet: £42.00 (30) | |||