Related guidance:
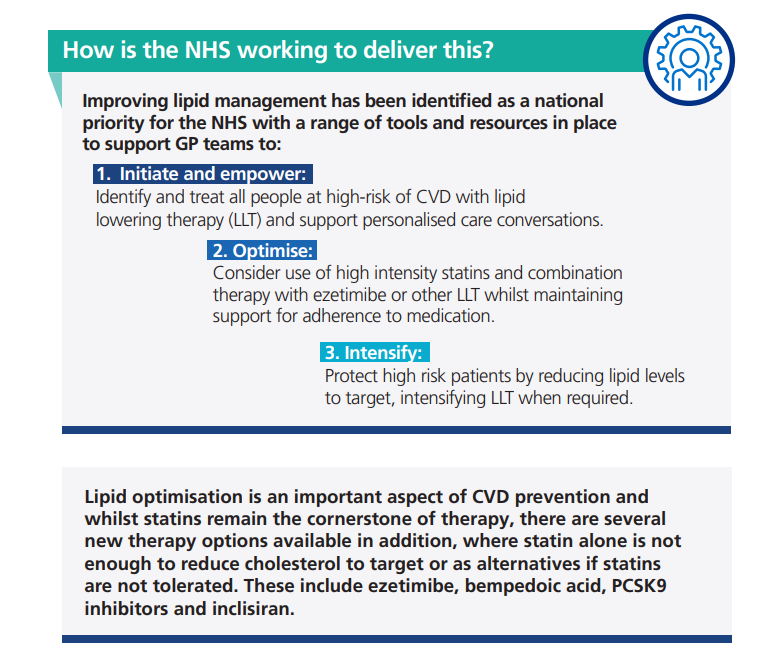
Improving lipid management to reduce cardiovascular disease and save lives (NHSE November 2023)
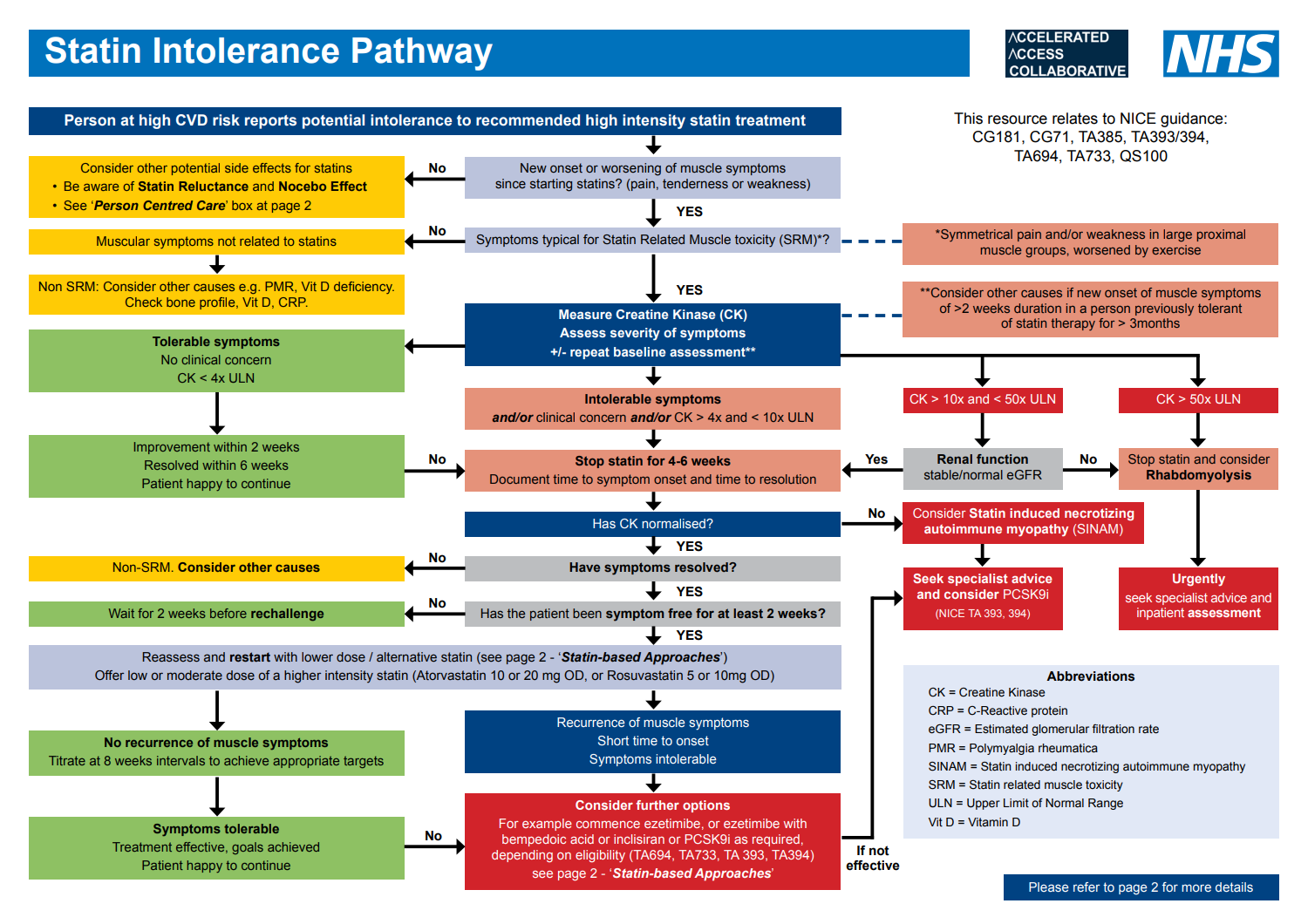
Statin Intolerance Pathway (NHSE August 2020, updated August 2023)
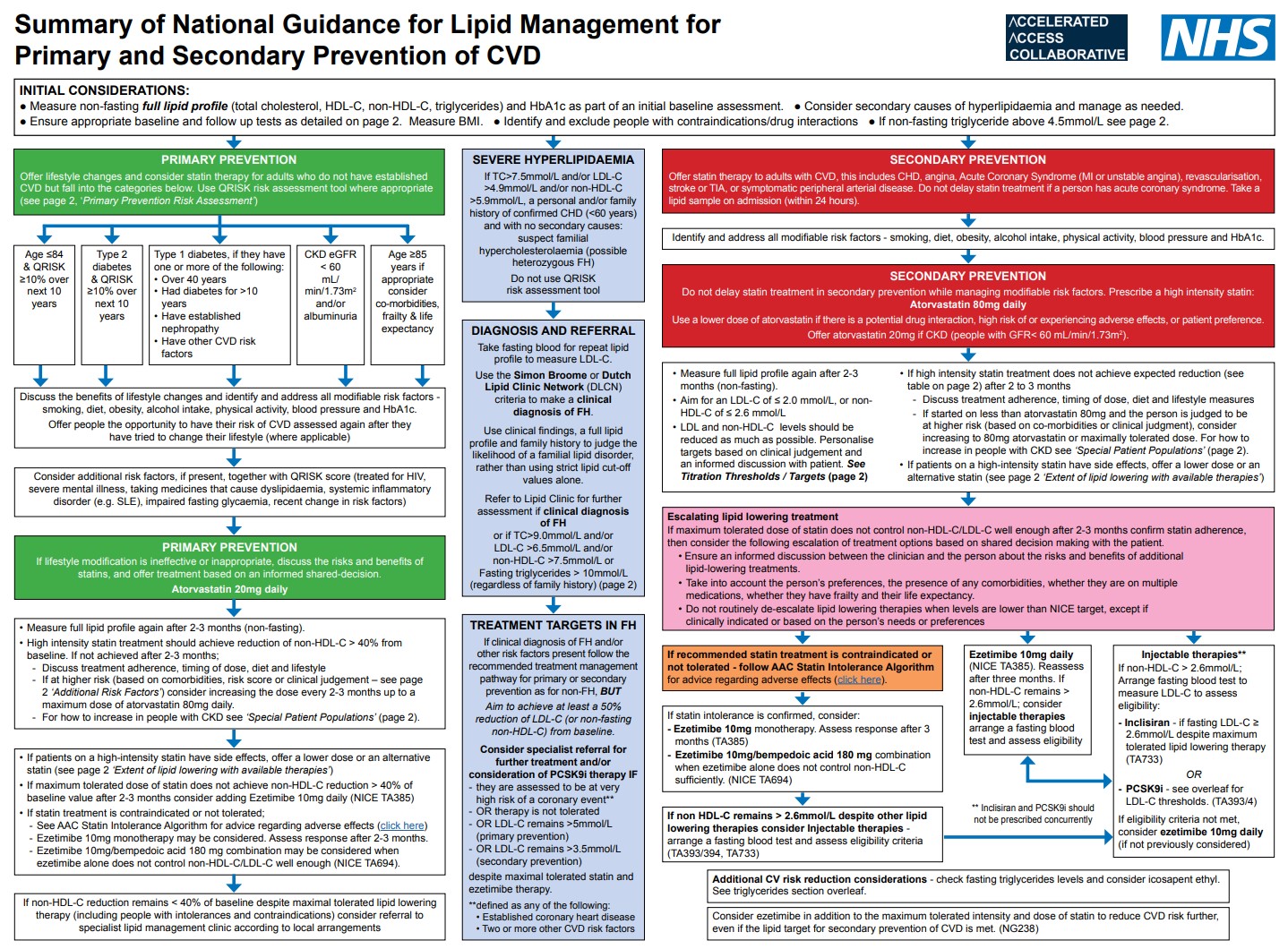
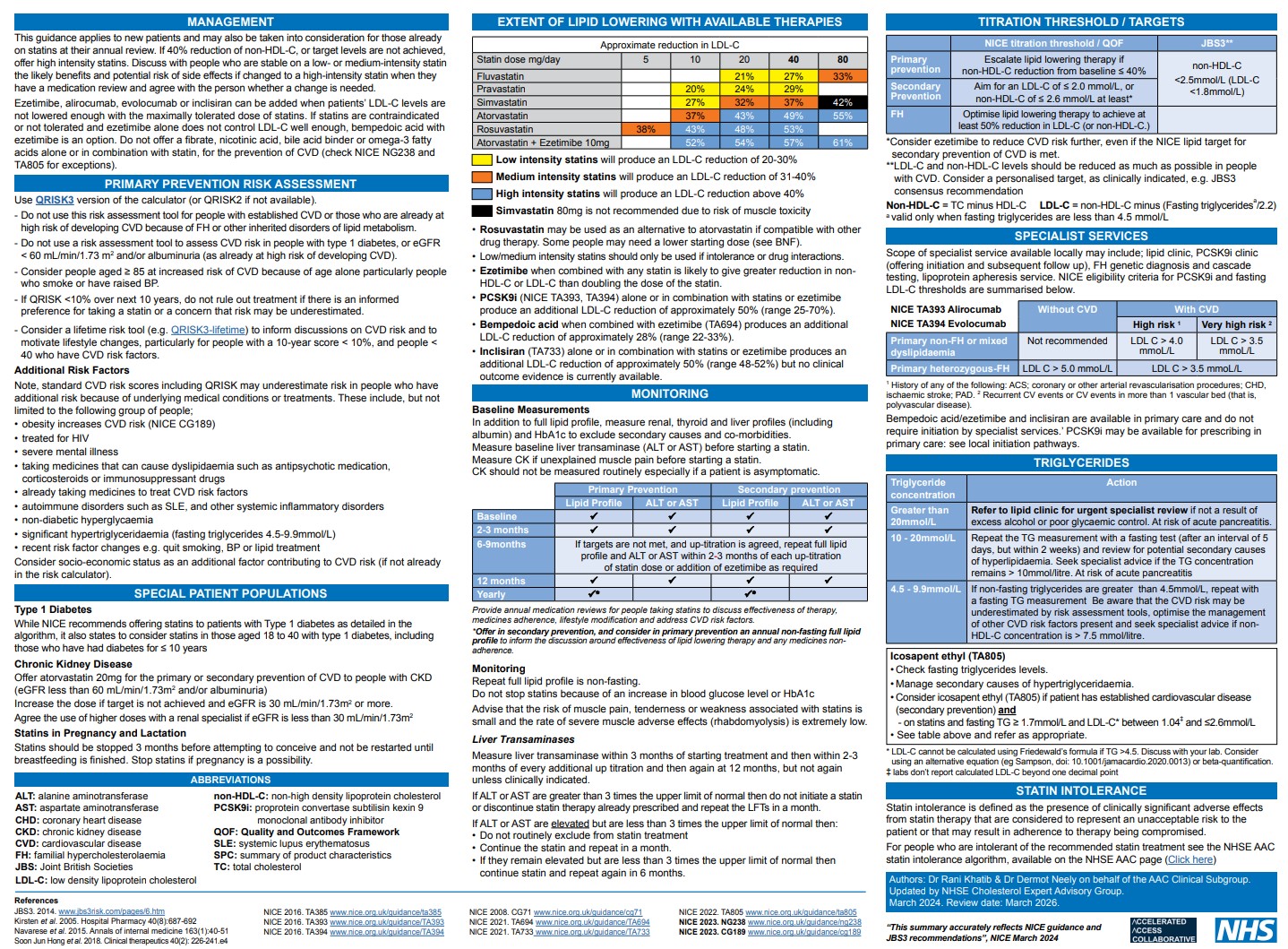
- Use the QRISK3 tool to calculate the estimated CVD risk within the next 10 years for people aged between 25 and 84 with type 2 diabetes and without CVD.
- Until electronic clinical systems in which QRISK2 is embedded are updated with QRISK3, it may be necessary to use QRISK2. When assessing risk for people taking corticosteroids or atypical antipsychotics or people with systemic lupus erythematosus, migraine, severe mental illness or erectile dysfunction, use QRISK3 (the online version of QRISK3, if necessary) because QRISK2 does not take these risk factors into account and so may underestimate the 10-year CVD risk in these populations.
- Do not offer omega 3 fatty acid compounds to prevent CVD.
- Do not offer nicotinic acid (niacin) to prevent CVD.
- Do not routinely offer fibrates to prevent CVD (except familial hypercholesterolaemia on advice by specialist).
- Do not offer a bile acid sequestrant (anion exchange resin) to prevent CVD (except familial hypercholesterolaemia on advice by specialist).
Lipid target for people taking lipid-lowering treatments
- For secondary prevention of CVD, aim for low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol levels of 2.0 mmol per litre or less, or non-HDL cholesterol levels of 2.6 mmol per litre or less.
Initial treatment
- Offer atorvastatin 80 mg to people with CVD, whatever their cholesterol level (off label), unless (see below and offer lower dose)
• it could react with other drugs
• there is a high risk of adverse effects
• the person would prefer to take a lower dose.
Consider ezetimibe in addition to the maximum tolerated intensity and dose of statin to reduce CVD risk further, even if the lipid target for secondary prevention of CVD is met.
Should I take a statin patient decision aid (QS100 updated
- What are heart disease and stroke?
- What is my risk of heart disease or stroke?
- What can I do to reduce my risk?
- How could a statin help?
- What does taking a statin involve?
- How much will a statin reduce my risk?
- What are the possible side effects of statins?
Acute coronary syndromes NICE guideline (NG185 November 2020)
- Do not offer or advise people to use the following to prevent another MI: omega-3-fatty-acid capsules.
Using lipid-lowering medicines during breastfeeding (SPS April 2023)
| Therapeutic Area | Formulary Choices | Cost for 28 (unless otherwise stated) | Rationale for decision / comments | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lipid modifying drugs | ||||
| Statins | Atorvastatin | 10mg tablet: £1.15 | First line statin for hypercholesterolaemia and prevention of cardiovascular events. Hypercholesterolaemia Adult:10 mg once daily, then increased to 40 mg once daily, dose to be increased at intervals of at least 4 weeks, then increased if necessary up to 80 mg once daily. Primary prevention Adult: 20 mg once daily; increased if necessary up to 80 mg once daily, dose to be increased at intervals of at least 4 weeks. Secondary prevention Adult: 80 mg once daily. | Before starting treatment with statins, at least one full lipid profile (non-fasting) should be measured, including total cholesterol, HDL-cholesterol, non-HDL-cholesterol (calculated as total cholesterol minus HDL-cholesterol), and triglyceride concentrations, thyroid-stimulating hormone, and renal function should also be assessed. Liver enzymes should be measured before treatment, and repeated within 3 months and at 12 months of starting treatment, unless indicated at other times by signs or symptoms suggestive of hepatotoxicity. Those with serum transaminases that are raised, but less than 3 times the upper limit of the reference range, should not be routinely excluded from statin therapy. Those with serum transaminases of more than 3 times the upper limit of the reference range should discontinue statin therapy. Before initiation of statin treatment, creatine kinase concentration should be measured in patients who have had persistent, generalised, unexplained muscle pain (whether associated or not with previous lipid-regulating drugs); if the baseline concentration is more than 5 times the upper limit of normal, a repeat measurement should be taken after 7 days. If the repeat concentration remains above 5 times the upper limit of normal, statin treatment should not be started; if concentrations are still raised but less than 5 times the upper limit of normal, the statin should be started at a lower dose. Some patients may present with an extremely elevated baseline creatine kinase concentration, for example because of a physical occupation or rigorous exercise—specialist advice should be sought regarding consideration of statin therapy in these patients. Patients at high risk of diabetes mellitus should have fasting blood-glucose concentration or HbA1C checked before starting statin treatment, and then repeated after 3 months. Hypothyroidism should be managed adequately before starting treatment with a statin. Statins should be avoided in pregnancy (discontinue 3 months before attempting to conceive) as congenital anomalies have been reported and the decreased synthesis of cholesterol possibly affects fetal development. |
| 20mg tablet: £1.22 | ||||
| 40mg tablet: £1.41 | ||||
| 80mg tablet: £2.49 | ||||
| Rosuvastatin | 5mg tablet: £1.01 | Rosuvastatin may be used as an alternative to atorvastatin if compatible with other drug therapy. Hypercholesterolaemia Adult: 5 mg once daily, then increased if necessary up to 20 mg once daily, dose to be increased gradually at intervals of at least 4 weeks. Maximum dose 40mg daily. Prevention of cardiovascular events Adult: 20 mg once daily (Asian/over 70 years/with risk factors for myopathy or rhabdomyolysis; initially 5 mg once daily, then increased if tolerated to 20 mg once daily, dose to be increased gradually at intervals of at least 4 weeks. Avoid if creatinine clearance less than 30 mL/minute. |
||
| 10mg tablet: £1.20 | ||||
| 20mg tablet: £1.61 | ||||
| 40mg tablet: £1.83 | ||||
| 5mg capsule: £8.52 | ||||
| 10mg capsule: £9.54 | ||||
| 20mg capsule: £12.72 | ||||
| 40mg capsule: £15.12 | ||||
| Simvastatin | 10mg tablet: £0.87 | Hypercholesterolaemia and prevention of cardiovascular events Adult: 20–40 mg to be taken at night. Manufacturer advises maximum of 20 mg daily with concurrent use of amiodarone, amlodipine, ranolazine, verapamil and diltiazem, bempedoic acid or bempedoic acid with ezetimibe. 80mg is not recommended due to risk of muscle toxicity. |
||
| 20mg tablet: £1.17 | ||||
| 40mg tablet: £1.06 | ||||
| 80mg tablet: £2.03 | ||||
| Pravastatin | 10mg tablet: £1.59 | Hypercholesterolaemia Adult: 10–40 mg to be taken at night, dose to be adjusted at intervals of at least 4 weeks. Prevention of cardiovascular events Adult: 40 mg to be taken at night. Manufacturer advises initial dose of 10 mg once daily in moderate to severe renal impairment. |
||
| 20mg tablet: £1.75 | ||||
| 40mg tablet: £1.98 | ||||
| NHS Somerset classify Fluvastatin as not recommended as per Traffic light guidance. | ||||
| There is an increased risk of myopathy associated with high-dose (80 mg) simvastatin. The 80-mg dose should be considered only in patients with severe hypercholesterolaemia and high risk of cardiovascular complications who have not achieved their treatment goals on lower doses, when the benefits are expected to outweigh the potential risks. See MHRA (May 2010) for Simvastatin: increased risk of myopathy at high dose (80 mg). | ||||
| Detailed recommendations for dose restrictions when used with some other drugs as interactions may increase the risk of adverse effects, or reduce the effectiveness of statin treatment. See MHRA (December 2004) for Statins: interactions, and updated advice for atorvastatin. | ||||
| Globally, there has been a very small number of reports of new-onset or aggravation of pre-existing myasthenia gravis with atorvastatin, pravastatin, lovastatin, fluvastatin, simvastatin, rosuvastatin and pitavastatin (single-ingredient and fixed-dose combination products). Advise patients taking statins to be alert to new symptoms for myasthenia gravis, or worsening symptoms of pre-existing myasthenia gravis, and to seek medical advice if these occur. See MHRA (September 2023) for Statins: very infrequent reports of myasthenia gravis. | ||||
| Cholesterol absorption inhibitors | Ezetimibe | 10mg tablet: £8.26 | NHS Somerset classify as green for hypercholesterolaemia. Monotherapy is recommended as an option for treating primary (heterozygous‑familial or non‑familial) hypercholesterolaemia in adults in whom initial statin therapy is contraindicated or who cannot tolerate statin therapy. Co‑administered with initial statin therapy, is recommended as an option for treating primary (heterozygous‑familial or non‑familial) hypercholesterolaemia in adults who have started statin therapy when: serum total or low‑density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol concentration is not appropriately controlled as per NICE either after appropriate dose titration of initial statin therapy or because dose titration is limited by intolerance to the initial statin therapy as per NICE and a change from initial statin therapy to an alternative statin is being considered. When prescribing ezetimibe co‑administered with a statin, ezetimibe should be prescribed on the basis of lowest acquisition cost. Healthcare professionals should offer adults with FH a referral to a specialist with expertise in FH if treatment with the maximum tolerated dose of a high-intensity statin and ezetimibe does not achieve a recommended reduction in LDL-C concentration of greater than 50% from baseline (that is, LDL-C concentration before treatment). Adult: 10 mg once daily. Manufacturer advises avoid in moderate to severe hepatic impairment. |
|
| NHS Somerset classify Ezetimibe and Simvastatin combination as not recommended as per Traffic light guidance. | ||||
| Adenosine triphosphate-citrate lyase inhibitors | Bempedoic acid as Nilemdo® | 180mg tablet: £55.44 | NHS Somerset classify as amber 1 for prescribing without formal shared care protocol, may be initiated by GP on trust advice for patients for treating primary hypercholesterolaemia or mixed dyslipidaemia intolerant to statins and ezetimibe. Adult: 180 mg daily. Liver function tests should be performed at initiation of therapy. Should be discontinued if an increase in transaminases of > 3× the upper limit of normal, persists. |
|
| Ezetimibe and Bempedoic acid as Nustendi® | 10/180mg tablet: £55.44 | NHS Somerset classify as green for treating primary hypercholesterolaemia or mixed dyslipidaemia. Adult: 180/10 mg daily. |
||
| PCSK9 protein inhibitors | Evolocumab as Repatha SureClick® | 140mg/1ml solution for injection pre-filled disposable device: £340.20 (2) | NHS Somerset classify as amber 2, appropriate for prescribing when specialist/trust initiated, without formal shared care protocol for treating primary hypercholesterolaemia or mixed dyslipidaemia, only if: the dosage is 140 mg every 2 weeks. Low-density lipoprotein concentrations are persistently above the thresholds specified as per NICE despite maximal tolerated lipid-lowering therapy. That is, either the maximum dose has been reached, or further titration is limited by intolerance. Adult: 140 mg every 2 weeks by subcutaneous injection. |
|
| Alirocumab as Praluent® | 75mg/1ml solution for injection pre-filled disposable device: £336.00 (1) | NHS Somerset classify as amber 2, appropriate for prescribing when specialist/trust initiate, without formal shared care protocol for treating primary hypercholesterolemia or mixed dyslipidaemia, only if: low-density lipoprotein concentrations are persistently above the thresholds specified as per NICE despite maximal tolerated lipid-lowering therapy. That is, either the maximum dose has been reached or further titration is limited by intolerance. Adult: Initially 75 mg by subcutaneous injection every 2 weeks; increased if necessary to 150 mg every 2 weeks, alternatively 300 mg every 4 weeks, patients requiring an LDL-C reduction of greater than 60% may be initiated on 150 mg every 2 weeks or 300 mg every 4 weeks, dose adjustments should be made at 4 to 8 weekly intervals. |
||
| 150mg/1ml solution for injection pre-filled disposable device: £336.00 (1) | ||||
| 300mg/2ml solution for injection pre-filled disposable device: £336.00 (1) | ||||
| mRNA PCSK9 protein inhibitors | Inclisiran as Leqvio® | 284mg/1.5ml solution for injection pre-filled syringe: £55.00 (as per reimbursement scheme) | NHS Somerset classify as green for treating primary hypercholesterolaemia or mixed dyslipidaemia as per NICE. Adult: Initially 284 mg by subcutaneous injection for 1 dose, followed by 284 mg after 3 months for 1 dose, then 284 mg every 6 months. |
|
| Ethyl eicosapentaenoic acids | Icosapent as Vazkepa® | 998mg capsule: £144.21 (120) | NHS Somerset classify as green for reducing the risk of cardiovascular events in adults. It is recommended if they have a high risk of cardiovascular events and raised fasting triglycerides (1.7 mmol/litre or above) and are taking statins, but only if they have: established cardiovascular disease (secondary prevention), defined as a history of any of the following: acute coronary syndrome (such as myocardial infarction or unstable angina needing hospitalisation), coronary or other arterial revascularisation procedures, coronary heart disease, ischaemic stroke, peripheral arterial disease, and low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL‑C) levels above 1.04 mmol/litre and below or equal to 2.60 mmol/litre. Adult: 1.996 g twice daily. |
|
| Omega-3-acid ethyl esters | Do not offer Omega 3 fatty acid compounds to prevent CVD. | |||
| Systematic reviews and meta-analyses of randomised controlled trials have highlighted a dose-dependent increased risk of atrial fibrillation in patients with established cardiovascular diseases or cardiovascular risk factors treated with omega-3-acid ethyl ester medicines compared to placebo. See MHRA (January 2024) for Omega-3-acid ethyl ester medicines (Omacor/Teromeg 1000mg capsules): dose-dependent increased risk of atrial fibrillation in patients with established cardiovascular diseases or cardiovascular risk factors. | ||||
| Fibrates | Fenofibrate | 67mg micronised capsule: £18.16 (90) | For familial hypercholesterolaemia. Adult: Once daily. Maximum 67 mg daily if eGFR 30–59 mL/minute/1.73 m2. Maximum 200 mg daily with concomitant statin. Manufacturer advises monitor hepatic transaminases every 3 months during the first 12 months of treatment and periodically thereafter—discontinue treatment if levels increase to more than 3 times the upper limit of normal; monitor serum creatinine levels during the first 3 months of treatment and periodically thereafter—interrupt treatment if creatinine level is 50% above the upper limit of normal. | Do not routinely offer fibrates to prevent CVD - on advice of lipid specialist only as per NICE. |
| 160mg micronised tablet: £3.36 | ||||
| 200 mg micronised capsule: £2.68 | ||||
| 267mg micronised capsule: £3.04 | ||||
| Bile acid sequestrants | Colestyramine as Questran® | 4g oral powder sachet: £10.76 (50) | NHS Somerset classify as amber 2, appropriate for prescribing when specialist/trust initiated, without formal shared care protocol for familial hypercholesterolaemia. Adult: 4 g daily, increased in steps of 4 g every week; increased to 12–24 g daily in 1–4 divided doses, adjusted according to response; maximum 36 g per day. | Do not routinely offer bile acid sequestrants to prevent CVD - on advice of lipid specialist only as per NICE. |
| Colesevelam | 625mg tablet: £66.25 (180) | NHS Somerset classify as amber 2, appropriate for prescribing when specialist/trust initiated, without formal shared care protocol familial hypercholesterolaemia. Adult: 2.5–3.75 g daily in 1–2 divided doses, may be taken at the same time as the statin and ezetimibe. |
||
| Nicotinic acid derivatives | Do not offer nicotinic acid (niacin) to prevent CVD as per NICE. | |||